What you need to know
to protect your family
Lead is a metal that our bodies don’t need. Exposure to lead can seriously harm your child’s health and future.
Lead exposure can cause:
Damage to the brain, nerves, and kidneys
Learning and behavior problems
Slowed growth and development
Hearing and speech problems
Most children show NO signs of lead poisoning.
Some symptoms may include stomach ache, fatigue, constipation, or irritability. Call your health care provider if you think your child may have lead poisoning.
Where lead lives
Lead can be found in many places.
Paint in homes built before 1978.
Clean and dust surfaces often. Don’t allow your child to play near old windows or in bare soil.
Water pumped through lead pipes.
Drink or cook with COLD water from the tap. Hot water can have higher levels of lead.
Certain toys and jewelry.
Watch what goes in your child’s mouth! Wash hands and toys often.
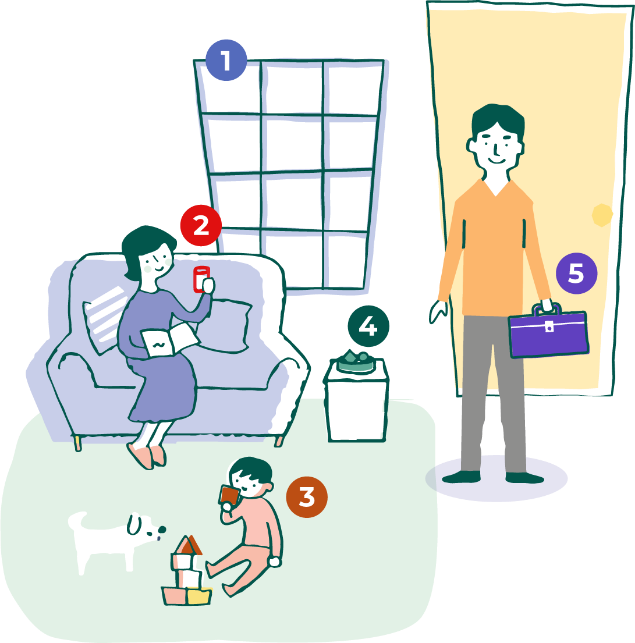
Traditional home remedies or imported items such as candies, makeup, or clay pottery may contain higher lead content which may be harmful to your child.
These items should be avoided or used as decoration only.
Some work environments may increase your exposure to lead-based products (building renovations, auto repair shops, etc.).
Take precautions and consider removing shoes before entering the home. Change clothing and shower to reduce lead exposure.
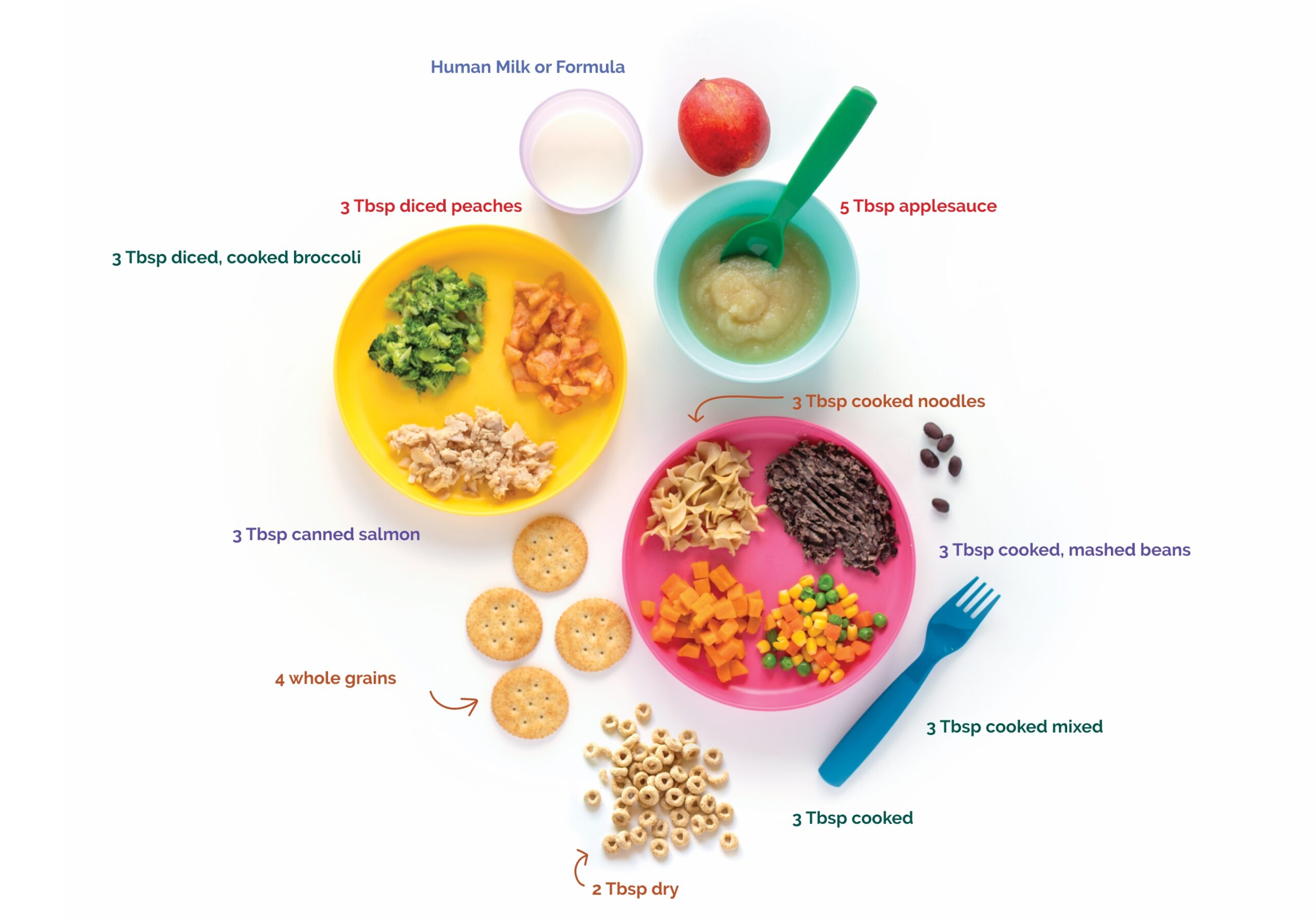
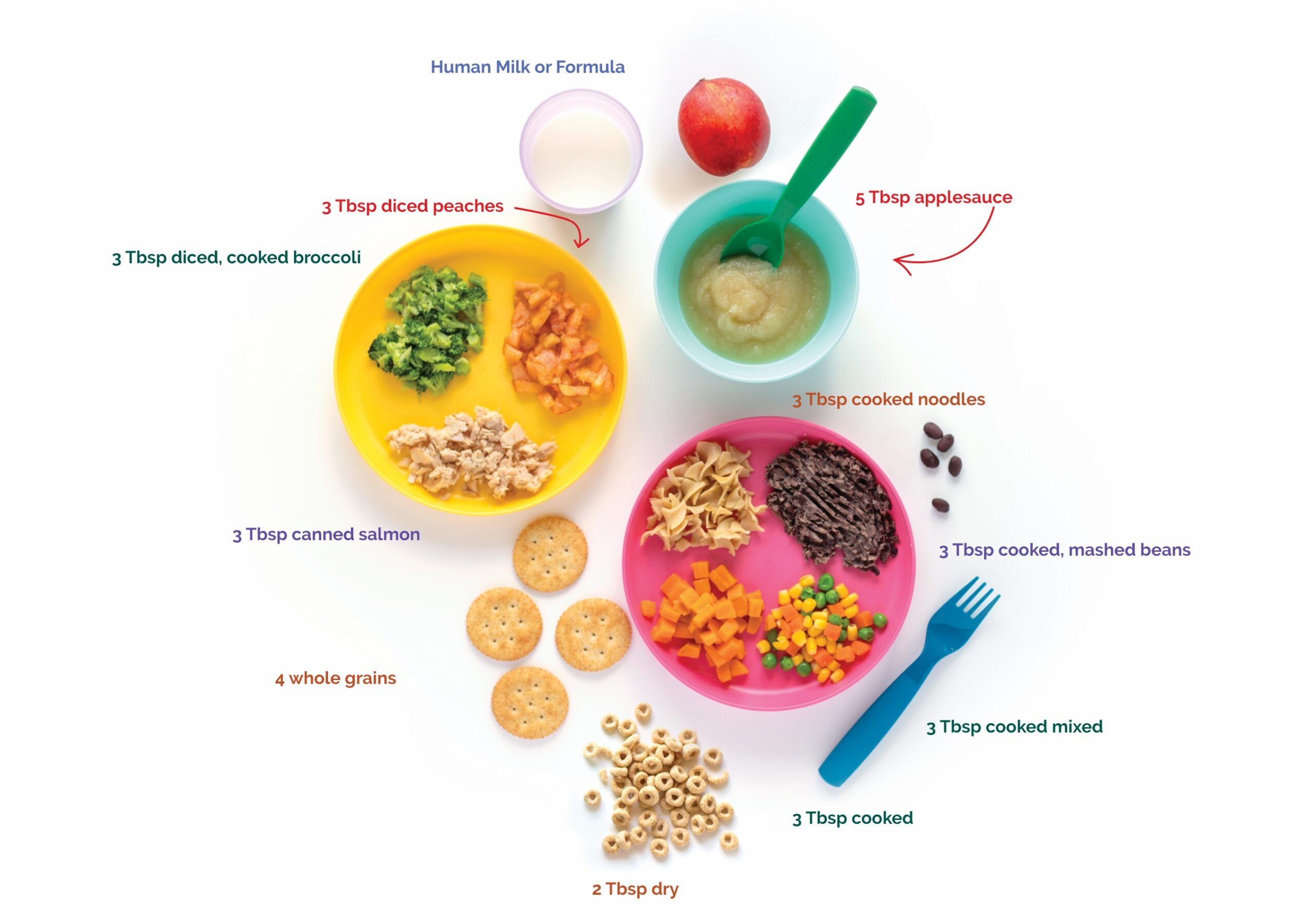
3 key nutrients
Calcium, Iron and Vitamin C
Good nutrition is another way to protect your family from lead.
For children and adults, three key nutrients can play a role in protecting the body from the harmful effects of lead:
CALCIUM
IRON
VITAMIN C
CALCIUM
IRON
VITAMIN C
These nutrients help the body absorb less lead and are part of a healthy diet. Choose a variety of foods daily!

Check for lead
Your health care provider can do a simple finger-prick test for lead.
Talk to your health care provider about getting your child tested for lead at age 1 and 2 years old.
What you need to know
to protect your family
Lead is a metal that our bodies don’t need. Exposure to lead can seriously harm your child’s health and future.
Lead exposure can cause:
Damage to the brain, nerves, and kidneys
Learning and behavior problems
Slowed growth and development
Hearing and speech problems
Most children show NO signs of lead poisoning.
Some symptoms may include stomach ache, fatigue, constipation, or irritability. Call your health care provider if you think your child may have lead poisoning.
Where lead lives
Lead can be found in many places.
Paint in homes built before 1978.
Clean and dust surfaces often. Don’t allow your child to play near old windows or in bare soil.
Water pumped through lead pipes.
Drink or cook with COLD water from the tap. Hot water can have higher levels of lead.
Certain toys and jewelry.
Watch what goes in your child’s mouth! Wash hands and toys often.

Traditional home remedies or imported items such as candies, makeup, or clay pottery may contain higher lead content which may be harmful to your child.
These items should be avoided or used as decoration only.
Some work environments may increase your exposure to lead-based products (building renovations, auto repair shops, etc.).
Take precautions and consider removing shoes before entering the home. Change clothing and shower to reduce lead exposure.
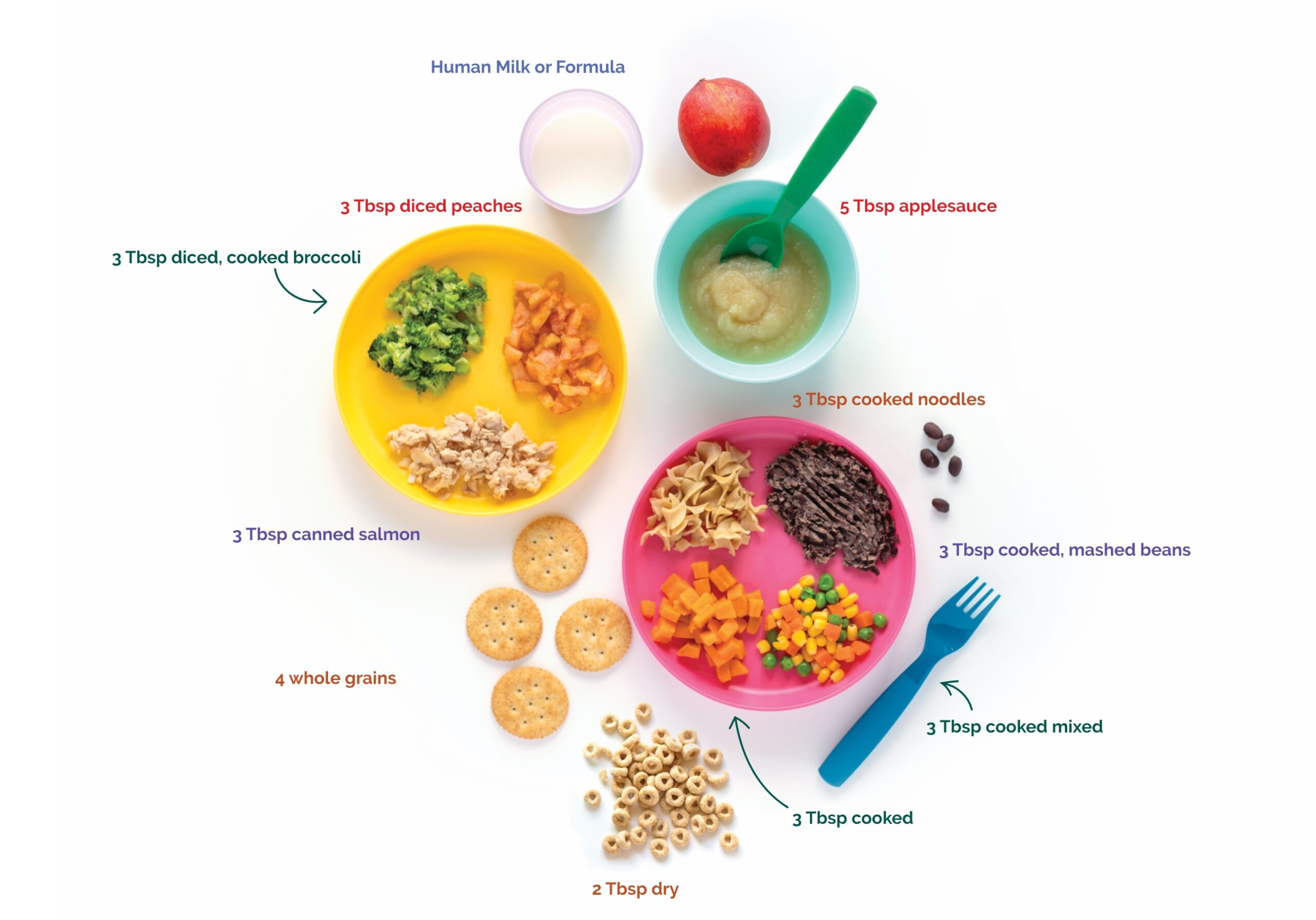
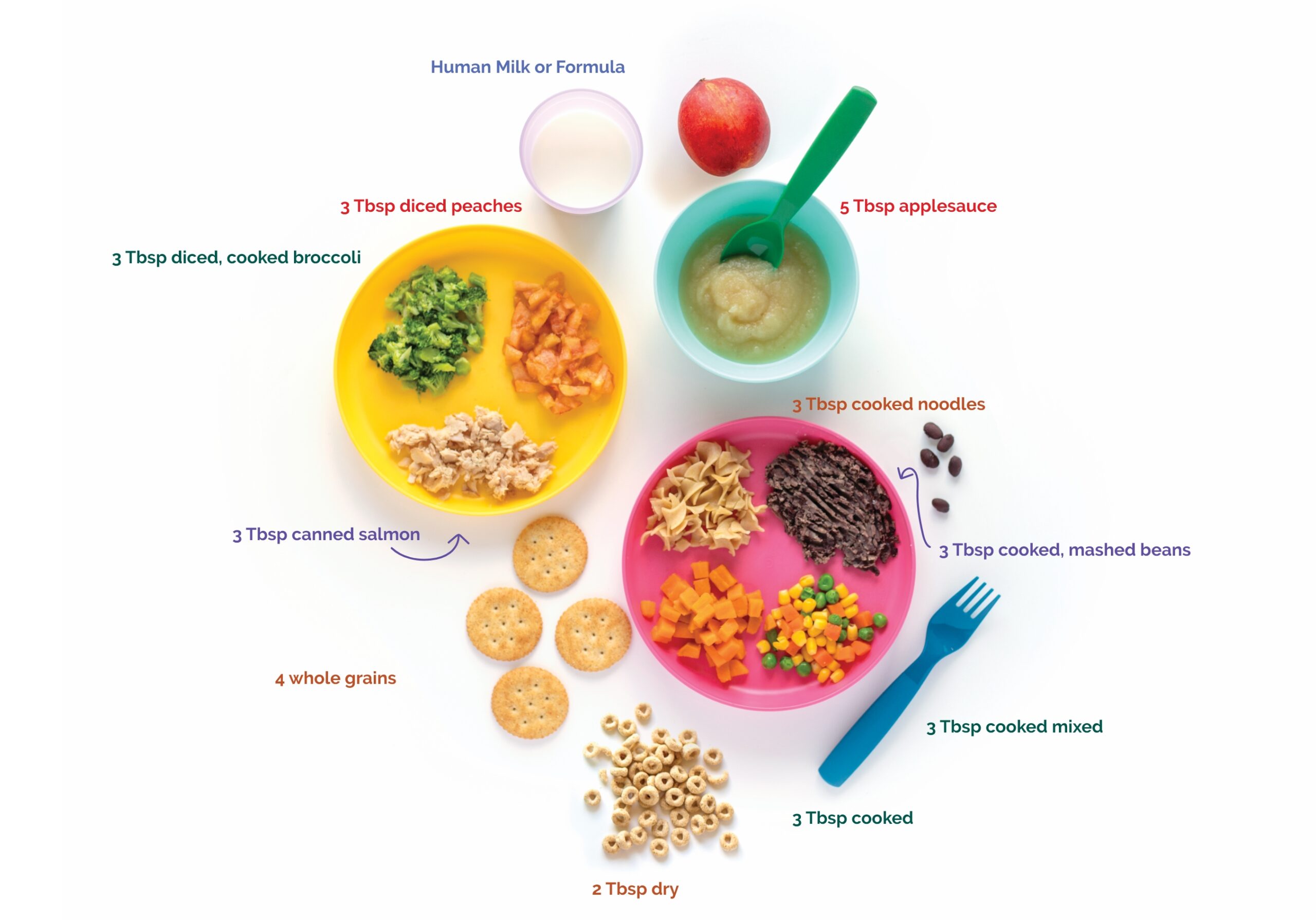
3 key nutrients
Calcium, Iron and Vitamin C
Good nutrition is another way to protect your family from lead.
For children and adults, three key nutrients can play a role in protecting the body from the harmful effects of lead:
CALCIUM
IRON
VITAMIN C
CALCIUM
IRON
VITAMIN C
These nutrients help the body absorb less lead and are part of a healthy diet. Choose a variety of foods daily!

Check for lead
Your health care provider can do a simple finger-prick test for lead.
Talk to your health care provider about getting your child tested for lead at age 1 and 2 years old.
Locations Providing Blood Lead Testing
New Castle County
Hudson State Service Center
Public Health Clinic
501 Ogletown Road
Newark, DE 19711
302-283-7587 ext. 3
Porter State Service Center
Public Health Clinic
509 W. 8th Street
Wilmington, DE 19801
302-777-2860
Kent County
Public Health Clinic
805 River Road
Dover, DE 19901
302-857-5140
Milford State Service Center at the Riverwalk
Public Health Clinic
253 NE Front Street
Milford, DE 19963
302-424-7140
Sussex County
Public Health Clinic
544 S. Bedford Street
Georgetown, DE 19947
302-515-3174
Anna C. Shipley State Service Center
Public Health Clinic
350 Virginia Avenue
Seaford, DE 19973
302-628-6772
























